ModSec is an open-source web application firewall which was designed for the apache server initially but now can be used for other different servers as well.ModSecurity is also known as ModSec and can filter HTTP requests and responses based on defined filtering rules. We will use the OWASP ModSecurity CORE RULE SET (CRS) here. We can also define our custom rules but that is a different topic.

I have just created a simple PHP page that will be used to verify credentials. Put this page in /var/www/html/login.php
Here is the page login.php:
<html>
<body>
<?php
if(isset($_POST[‘login’]))
{
$username = $_POST[‘username’];
$password = $_POST[‘password’];
$connection = mysqli_connect(‘localhost’,’root’,’test’,’testdb’);
$result = mysqli_query($connection, “SELECT * FROM `users`
WHERE username=’$username’ AND password=’$password’”);
if(mysqli_num_rows($result) == 0)
echo ‘Wrong Credentials’;
else
echo ‘<h1>Log in Successful</h1>’;
}
else
{
?>
<form action=”” method=”post”>
Enter the Username: <input type=”text” name=”username”/><br />
Enter the Password: <input name=”password” type=”password”/><br />
<input type=”submit” value=”Login” name=”login”/>
</form>
</body>
</html>

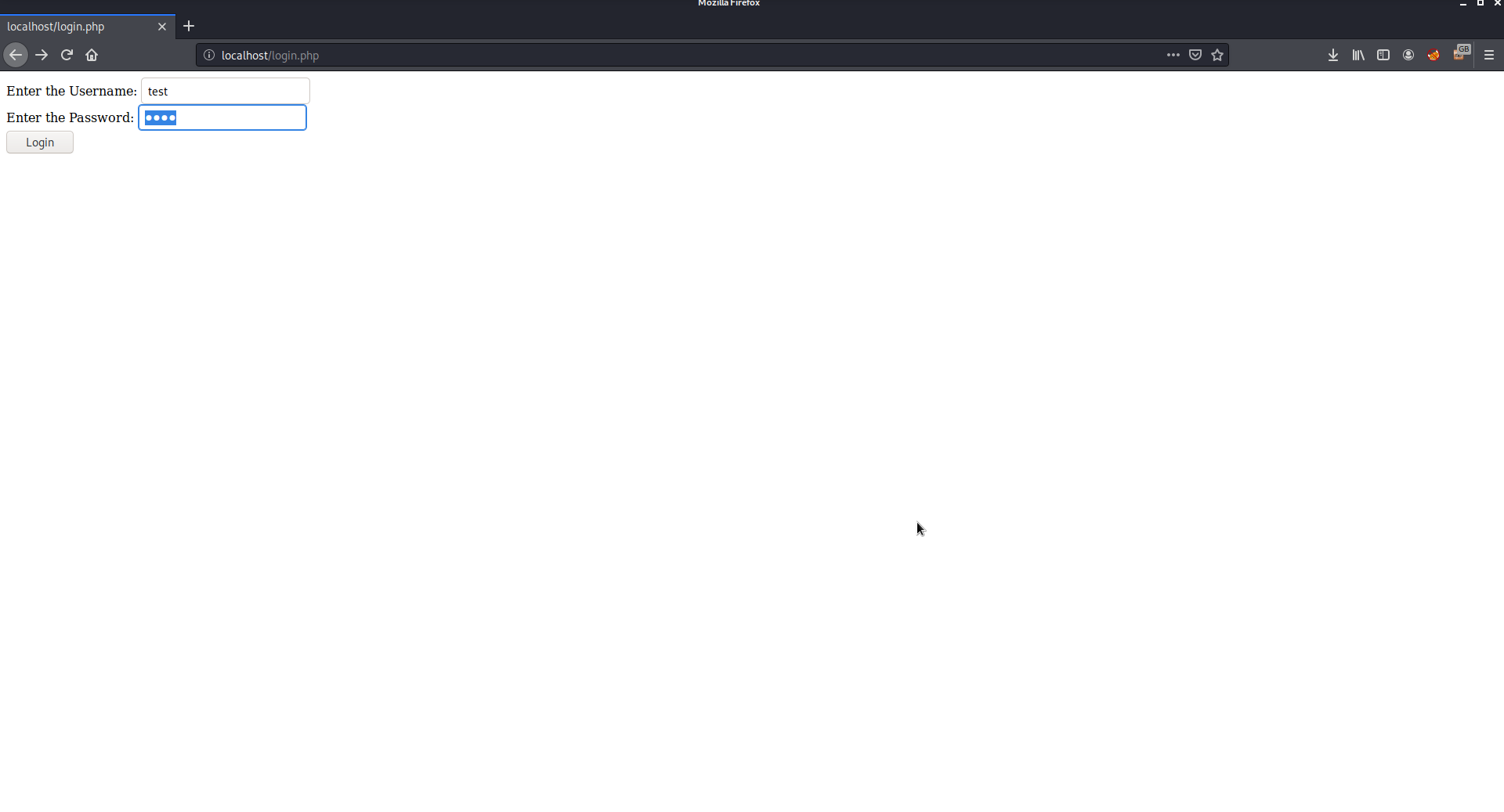
Now you need to create a database and a table for the page using MySQL.

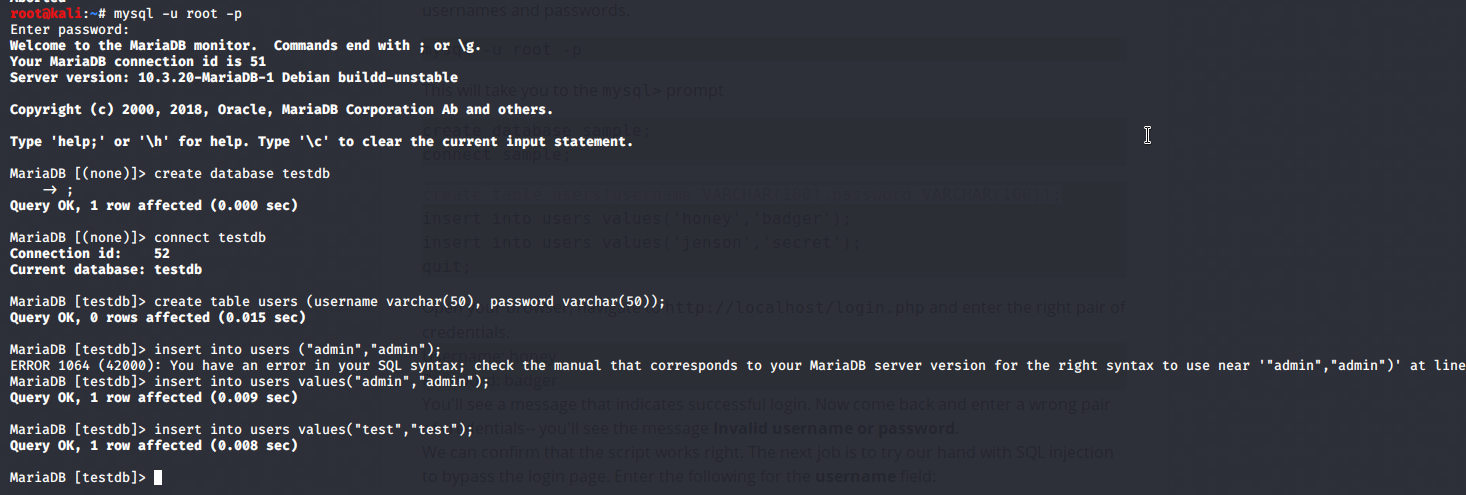
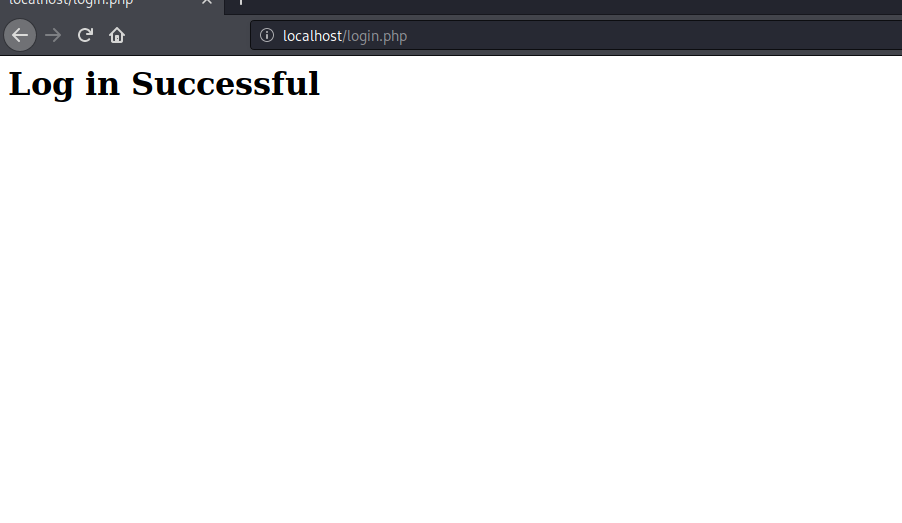
Now use the credential you just stored in the database and you will get logged in.

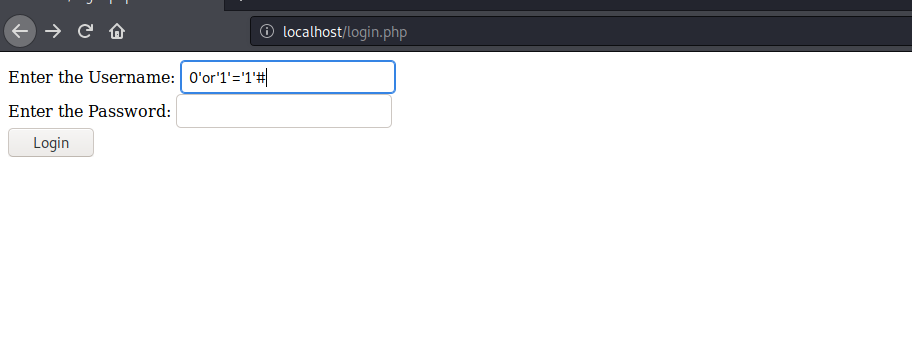
Now try to do SQL injection and you will be able to get through.



Now to prevent such attacks we need to configure the firewall
Configuring the Modsec firewall
Now to configure Modsec WAF follow the steps:
1. cd to /etc/apache2/ and create a folder named “modsecurity.d”
2. You need to clone OWASP rules or policies which contains the filters or rules or policies for the OWASP vulnerabilities using
Command: git clone https://github.com/SpiderLabs/owasp-modsecurity-crs.git
3. The above command will create a folder owasp-modsecurity-crs/
(Here you can read a file named INSTALL in this directory to read
instructions on how to configure Modsec on different servers.)
4. Go inside owasp-modsecurity-crs/ and rename crs-setup.conf.example file to crs-setup.conf
5. Now go further into rules folder and rename REQUEST-900-EXCLUSION-RULES-BEFORE-CRS.conf.example to REQUEST-900-EXCLUSION-RULES-BEFORE-CRS.conf
6. Rename RESPONSE-999-EXCLUSION-RULES-AFTER-CRS.conf.example to RESPONSE-999-EXCLUSION-RULES-AFTER-CRS.conf
7. Goto /etc/apache2.conf and add the following lines into the end of the document
<IfModule security2_module>
Include modsecurity.d/owasp-modsecurity-crs/crs-setup.conf
Include modsecurity.d/owasp-modsecurity-crs/rules/*.conf
</IfModule>
This will instruct the apache from where to pick up the rules.
8. restart apache service to make the rules come to effect.
Command: service apache2 restart
This will configure the WAF for you and now try opening the web application.
Use the same injection command used above and you will not be able to login now and will show the page lime this:


If you get an error restarting apache then it means your WAF is not properly configured.
Note if you get any problem using MySQL, restart the MySQL service using
service MySQL restart
Comments
Post a Comment